Contents
Experts estimate that up to 80 percent of the population will experience back pain at some time in their lives. The problem can be treated with a non-invasive and drug-free alternative called Chiropractic. Find your nearest chiropractor for your back pain problem today!
1. What is low back pain?
Low back pain can be an ongoing or chronic problem for many people. It can be caused by tendons, ligaments, vertebrae, discs, nerves, and extra-spinal factors that induce discomfort in the lower back. The nature and frequency of pain will vary depending on the severity of the condition.

Individuals between 30 and 50 years old are more prone to experience low back discomfort. This is partly due to changes in the body as we age. The fluid content between the vertebrae in your spine decreases as you become older.
2. Types of Low Back Pain
Low Back Pain types fall into three categories:
- Acute low back pain lasts from several days to 4 weeks.
- Subacute low back pain lasts from 4 to 12 weeks.
- Acute low back pain can develop into chronic low back pain lasting more than 12 weeks.
3. Some common symptoms of low back pain
Low back pain symptoms might appear unexpectedly and go away on their own, or they can worsen over time. The following are some of the most prevalent symptoms of low back pain:
- In the lower back, there is a dull ache.
- There is a sharp, burning feeling from the waist to the back of the thigh. It can also migrate to the lower leg or foot, causing numbness or tingling.
- Tension in the lower back, pelvis, and hips, as well as a muscle sphincter.
- Lower back discomfort worsens when you sit or stand for lengthy periods.
- Standing or walking is difficult, as are shifting postures when walking, sitting, or lying down.
4. What are the causes of low back pain?
Low back discomfort is frequently linked to the degenerative spinal disease, occurring when the spine’s bones, joints and discs lose their natural structure and function with time. The following are some examples of mechanical reasons for lower back pain:
4.1. Muscle strains
Back strains are a common cause of low back pain. Excessive pressure can strain or tear the muscles and ligaments in your back. Lower back discomfort and stiffness, as well as muscle spasms, are common symptoms. These symptoms can be managed with rest and physiotherapy.
4.2. Disc herniation
There are shock absorbers between all vertebrae of the spine. They are called intervertebral discs. With age or injury, an outer layer of a disc might rupture or herniate, causing the jelly-like substance inside to go out of its natural position and press against the spinal cord or nerve roots. This condition is called a disc herniation. Unlike muscle strain, a herniated disc can cause discomfort that lasts more than 72 hours.
The spine is a series of vertebrae and intervertebral discs. Once the intervertebral disc weakens and loses its normal function, it starts to bulge. The bulging disc can worsen with time and cause the nucleus pulposus to break through, putting pressure on the nerves. This is called a disc herniation.…
4.3. Spinal stenosis

Spinal stenosis occurs most often in the lower back region. It is most commonly caused by wear-and-tear and changes in the spine related to osteoarthritis. The condition narrows the spinal cord, which can put pressure on the nerves that travel through the spine.
4.4. Abnormal curvatures of the spine
Scoliosis, kyphosis, and lordosis are all conditions in which the spine curves abnormally. Because it puts strain on muscles, tendons, ligaments, the unusual curvature can lead to discomfort and poor posture.
Some of other causes of low back pain are injuries, traumas, prolonged bad postures, or even lack of proper exercises.
5. Complications
Low back pain may result in various complications, depending on the primary disease or condition. Over time, back pain may lead to complications, including:
- Chronic pain or inconvenience.
- Damage of nerves (due to pinched nerve), including paralysis.
- Permanent physical disorder.
- Physiological and psychological response to chronic pain.
- Poor life quality.
6. How is low back pain diagnosed?
To determine the severity of back pain, your doctor may request some kinds of imagings and reports, for instance:
- Blood Test: Evaluate the body’s inflammation if the patient is suspected of low back pain due to infection or cancer.
- X-ray: The initial diagnostic method helps show the abnormalities in your bone structure.
- Magnetic Resonance Visualization (MRI): Very useful and high-precision means to detect abnormalities in soft tissues such as muscle, ligament, discs.
- Computed tomography: CT scan results allow the doctor to see the spine from different angles, so damages to the bones and soft tissues within the spine can be detected quickly.
- Electromyography (EMG): This technique measures electrical impulses generated by nerves to help detect nerve compression due to disc herniation or spinal stenosis.
- Measurement of Bone Density: Patients may experience back pain due to osteoporosis. A bone density report helps doctors rule out this cause.
7. How to treat low back pain?
To relieve symptoms for low back pain, you can:
7.1. Home care
Home treatments should be used within the first 72 hours after the onset of pain. If pain persists after 72 hours of home treatment, the patient should see the nearest health care provider and find a suitable treatment as soon as possible. Below are a few ways to help you manage low back pain at home.
- Temporarily stop any intense physical activities for a few days and opt for light movements instead. Try to be mindful of your daily activities to avoid aggravating the pain. You can apply ice to the painful area. Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may provide you with short-term relief from pain.
- Low back pain can be uncomfortable when lying on your back. So, try lying on your side with your knees bent and a pillow between your legs. If you are comfortable lying on your back, place a pillow or dry towel under your hips to relieve pressure on your lower back. You can even take a warm bath or regularly massage the painful area to relieve muscle tensions.
>> More information: Proper sleeping position – Relieve the pain
7.2. Medical treatment

If your back pain doesn’t improve with over-the-counter medications, you may need more potent pain relievers. Many people choose to rely on drugs and medications; however, those are not always the solutions to this type of problem.
>> More information: How to treat lower back pain without drug
7.3. Surgery
For a severe case of back pain, your health care provider might recommend surgery. Surgery is often the last resort when other medical procedures have failed or when the patient has complications, such as severe spinal cord compression. There are many surgical methods to treat low back pain depending on the cause of pain, including spinal decompression or artificial disc replacement.
7.4. Chiropractic & physical rehabilitation
The causes of low back pain are mainly due to the musculoskeletal system. Medications can only provide temporary pain relief; however, they can cause gastrointestinal problems. Similarly, surgery can lead to many potential risks and is generally quite expensive.
To overcome the shortcomings of these two treatments, many health care providers have taken a new direction via chiropractic care. The ACC Chiropractic Clinic is proud to be the pioneer of chiropractic care in Vietnam. ACC’s treatment for low back pain combines chiropractic adjustments with physical therapy and rehabilitation programs tailored to each patient’s condition.
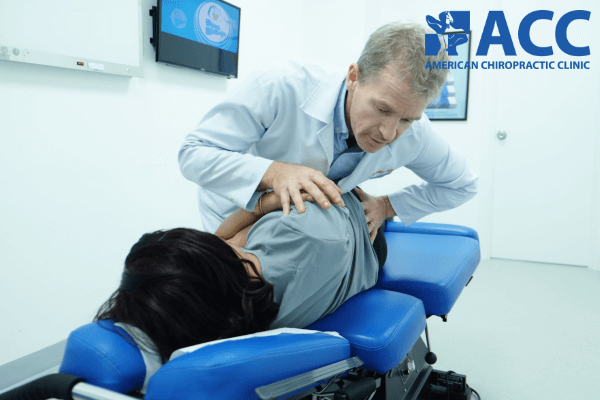
With the effective and holistic approach we provide at ACC, our patients can rest assured to overcome their conditions without drugs or surgery. The quality of our service is presented through cutting-edge technology. ACC is the only clinic in Southeast Asia to have Pneumex Pneuback – the most advanced and effective exercise system for spinal and muscular conditions. This seven-step exercise system helps our patients regain their functional abilities and ensures a speedy and successful recovery to their daily lives.
8. How to prevent low back pain?
To prevent the risk of low back pain, here are a few things you should keep in mind:
- When lifting heavy objects, don’t bend over from the waist. Bend your knees and squat, pulling in your stomach muscles and holding the object close to your body as you stand up. Let your legs do the lifting, not your back.
- Remember to maintain a straight back while sitting or standing. Good posture prevents pressure on the spine, therefore preventing pain and discomfort. Try to be mindful of your posture throughout the day and correct it when you notice your posture changes. Another thing to keep in mind, especially for office workers, is the ergonomy of your workspace. Try setting up your computer screen or chair at the proper height to avoid tension on your joints and muscles.
- Remember to rest. After every hour of sitting, you should stand up and stretch. Walk around or perform light movements to loosen up tight muscles and stiff joints.
- Pay attention to your diet and watch your weight. Extra weight can put extra pressure on your spine. Therefore, staying within 10 pounds of your weight may help control back pain. Additionally, you can prevent back pain by adding more food that has calcium, magnesium, and potassium to your daily meals.
- Get more exercise. Working out more and being active in general can help you relieve and reduce back pain. Try to exercise for at least 30 minutes every day, with proper warm-up and cool-down.
- Get routine checkups. It is necessary to have a checkup routine every six months. This allows you and your doctor to recognize any early signs of the illness and take steps to prevent it from becoming severe.
Read more: > Tips to prevent back pain while working from home > Exercises for easing and preventing upper back pain
9. The bottom line
Low back pain is a progressive condition and can become severe without proper care and treatment. By strengthening, stretching, and protecting your back, you can stop or prevent the discomfort. However, lifestyle adjustments may not always be sufficient in complicated or severe cases. Low back pain can be an early sign of many other musculoskeletal problems. If you recognize persistence or exacerbation of pain, contact the nearest ACC for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.