Contents
- 1. What Is Musculoskeletal Pain? What Are the Symptoms?
- 2. Common Types of Musculoskeletal Pain
- 3. What Are the Causes of Musculoskeletal Pain?
- 4. How Long Does Musculoskeletal Pain Last? When Should You See a Doctor?
- 5. How Is Musculoskeletal Pain Diagnosed?
- 6. How Is Generalized Musculoskeletal Pain Treated?
- 7. How to Prevent Musculoskeletal Pain
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions About Generalized Musculoskeletal Pain
- 8.1. Why Is Musculoskeletal Pain Becoming More Common Among Young People?
- 8.2. How Can Musculoskeletal Pain Be Reduced at Night?
- 8.3. Where Should I Go for an Examination If I Have Generalized Muscle Pain?
- 8.4. Can Generalized Musculoskeletal Pain Resolve on Its Own?
- 8.5. What Are the Possible Complications If Musculoskeletal Pain Is Left Untreated?
- 9. ACC Advice
Many people believe that generalized Musculoskeletal pain only affects older adults due to age-related degeneration of the musculoskeletal system. However, this condition is increasingly common among younger individuals. If left untreated, it may lead to serious health complications later in life.
1. What Is Musculoskeletal Pain? What Are the Symptoms?
Musculoskeletal pain refers to discomfort or pain affecting the muscles, bones, joints, ligaments, and tendons. One of the most noticeable symptoms is widespread pain involving multiple areas of the body, such as the neck, shoulders, back, arms, and legs.
Generalized Musculoskeletal Pain may occur at any time of the day but is most commonly experienced in the morning, at night, after intense physical activity, or following prolonged periods of sitting or standing. In addition, many individuals report associated symptoms such as insomnia, loss of appetite, persistent fatigue, and reduced quality of life.

2. Common Types of Musculoskeletal Pain
There are six common types of musculoskeletal pain: sudden pain, chronic pain, bone pain, etc. The detailed signs of each type of musculoskeletal pain are as follows:
- Sudden pain: The pain appears quickly, and can be sharp or intense. It often occurs after an accident or injury.
- Chronic pain: The pain is persistent and long-lasting, often related to arthritis or fibromyalgia. It can also stem from old injuries that haven’t healed or haven’t been properly treated.
- Bone pain: Usually a dull, deep ache. If a bone is fractured, the pain is usually more intense and sharp.
- Joint pain: Can occur continuously or in episodes. Joints may be stiff, aching, or feel hot and burning. In most cases, the pain decreases with rest and increases with movement.
- Muscle pain: Can be a persistent dull ache or a sharp, intermittent ache. Some people experience generalized pain, while others only experience pain in a few specific areas.
- Tendon and ligament pain: The pain usually increases with movement of the injured area, feeling sharp and uncomfortable.
3. What Are the Causes of Musculoskeletal Pain?
Generalized Musculoskeletal Pain may result from environmental and lifestyle factors, such as weather changes, a sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition, or frequent use of high-heeled shoes. In addition, it can be a symptom of various medical conditions, including spinal degeneration, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and other musculoskeletal disorders.
3.1. Environmental and Lifestyle-Related Causes
Living conditions, daily habits, diet, and physical activity levels play a crucial role in musculoskeletal health. Key contributing factors include:
- Sudden Weather Changes: Abrupt changes in temperature, air pressure, and humidity-especially during cold weather when atmospheric pressure increases and humidity decreases-can cause muscles and joints to contract and relax excessively. This may lead to thickening of synovial fluid, resulting in joint stiffness, dryness, and sharp pain.
- Prolonged Sitting and Lack of Physical Activity: This is a common cause of joint and back pain, particularly among young adults and office workers. Sitting for long periods in one position places continuous pressure on the hips and pelvis, leading to spinal stiffness and increasing the risk of spinal degeneration, disc herniation, bone spurs, and sciatica.

- Incorrect posture during exercise: Although physical activity is beneficial for overall health, performing exercises with improper posture can have the opposite effect, leading to musculoskeletal pain. Other poor postural habits that negatively affect the musculoskeletal system include slouching, sitting with crossed legs, and standing with a hunched back.
- Poor nutrition: A daily diet low in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids-resulting in a deficiency of important anti-inflammatory compounds-combined with excessive intake of salt and sugar can impair calcium absorption. Over time, this calcium deficiency negatively affects the musculoskeletal system and contributes to progressively worsening joint pain.
- Excessive alcohol and stimulant use: Alcohol and stimulants adversely affect the body’s metabolic processes, particularly calcium metabolism and absorption. This weakens bones and joints, making them more susceptible to pain and injury.
- Overweight and obesity: Each individual’s bones and joints are designed to support a certain amount of body weight. When body weight exceeds this limit, the musculoskeletal system is placed under excessive stress, significantly increasing the risk of generalized joint and bone pain.
- Frequent use of high heels: Wearing high heels shifts most of the body’s weight onto the forefoot, often causing toe pain. Over time, this places excessive strain on the ankle joints, increasing the risk of chronic osteoarthritis. Additionally, prolonged high-heel use may lead to pelvic misalignment.
- Chronic stress: Psychological stress is a significant but often overlooked factor affecting musculoskeletal health. Individuals who experience prolonged stress may not only feel exhausted and lack energy but also develop muscle tension, joint fatigue, and persistent pain.
>> Read more: What to Eat and Drink for Healthy Bones and Joints?

3.2. Causes Due to Pathological Conditions
Generalized bone and joint pain may be an early warning sign of several serious medical conditions, including:
- Spinal Degeneration: Spinal degeneration is a chronic condition, most commonly presenting as osteoarthritis of the spine. Typical symptoms include dull aching pain, limb weakness or numbness, and stiffness in the back, neck, or shoulders. Pain associated with spinal degeneration may appear suddenly and then subside, or persist continuously for several hours or even days. Without timely treatment, the condition may progressively worsen.
- Joint Degeneration: Joint degeneration is one of the most common causes of bone and joint pain. It occurs when the articular cartilage gradually wears down and can no longer adequately cushion the ends of the bones. As a result, bones rub against each other during movement, leading to pain, inflammation, and swelling. Pain typically worsens with activity and improves with rest, and symptoms often become more pronounced during weather changes—especially in cold conditions.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory joint disease, commonly caused by dysfunction of the immune system. Typical symptoms include recurrent joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and inflammation, which significantly interfere with movement and daily activities. If left untreated, rheumatoid arthritis may lead to muscle wasting and permanent joint deformities.
- Herniated Disc: A herniated disc is one of the most common musculoskeletal conditions, often presenting as dull, aching pain in the joints, particularly in the cervical and lumbar spine. This condition occurs when the intervertebral disc protrudes or ruptures, allowing the nucleus pulposus to bulge outward and compress the spinal canal and nerve roots, resulting in persistent, deep pain.
>> Read more: Lumbar disc herniation in young age
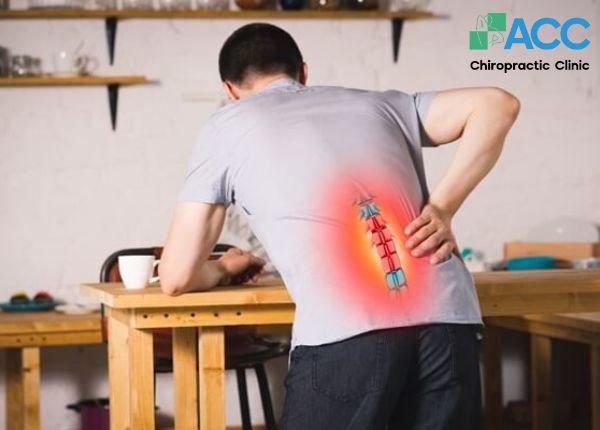

- Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis is a common cause of Musculoskeletal Pain in older adults. Patients often experience diffuse aching pain along the bones, especially near the ends of long bones. If not treated in time, the bones gradually become weaker and more fragile, significantly increasing the risk of fractures.
- Joint Tuberculosis: Joint tuberculosis, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, may lead to joint pain accompanied by swelling but typically without redness or warmth. Patients often have difficulty walking, bending, or straightening the affected limbs. The disease progresses slowly, and early symptoms are often subtle, making early diagnosis challenging. In advanced stages, joint tuberculosis can cause severe complications such as limb paralysis, vertebral collapse, and bone deformities.
- Gout: Generalized Musculoskeletal Pain may also be a manifestation of gout, which results from impaired purine metabolism and reduced uric acid excretion by the kidneys. This leads to the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, causing intense pain and inflammation. Gout attacks often worsen at night and may be accompanied by headaches, high fever, fatigue, and systemic discomfort.
- Infectious Arthritis: Infectious arthritis is an inflammation of the joint caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other microorganisms. These pathogens may enter the joint through penetrating injuries or spread via the bloodstream from infections elsewhere in the body. The condition most commonly affects the knee, but can also involve the shoulder, wrist, or ankle joints.
4. How Long Does Musculoskeletal Pain Last? When Should You See a Doctor?
Chronic, generalized musculoskeletal pain may persist for three months or longer. In general, the duration of pain depends on its underlying cause, severity, and the treatment approach applied.
If pain progressively worsens or is accompanied by any of the following warning signs, you should seek medical evaluation as soon as possible:
- Pain lasting longer than one week
- Joint swelling and redness
- Severe joint pain with difficulty moving
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Abdominal pain
- Digestive disturbances
- Unexplained weight loss
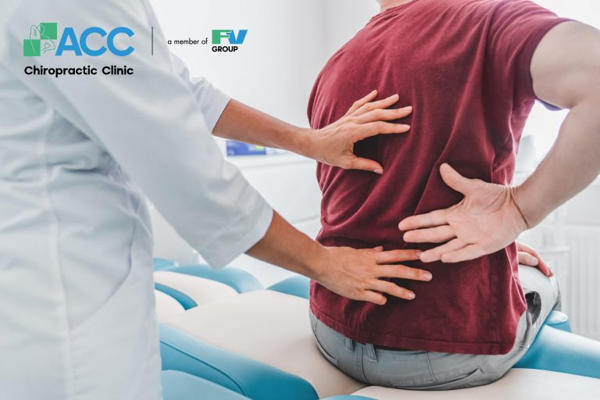

5. How Is Musculoskeletal Pain Diagnosed?
To identify the cause of musculoskeletal pain, doctors begin with a thorough clinical examination, followed by appropriate diagnostic tests as needed.
Clinical Evaluation
During the consultation, your doctor may ask questions such as:
- When did the pain begin?
- What were you doing at the time (e.g., exercising or playing sports)?
- How does the pain feel-sharp, burning, aching, tingling, or numb?
- Where is the pain located?
- Are there any accompanying symptoms such as fatigue or sleep disturbances?
- What activities or positions make the pain better or worse?
In addition, the doctor may gently press on or move the affected areas through various positions to accurately identify the source of pain.
Diagnostic Tests
Depending on the clinical findings, the doctor may recommend one or more of the following tests:
- X-ray or CT scan to assess bone structure
- MRI or ultrasound to evaluate soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments, and tendons
- Bone scan to detect abnormalities in bone metabolism or structure
- Myelogram, an imaging test that provides detailed visualization of the spinal cord and nerve roots
Blood and Other Tests
- Blood tests to detect signs of inflammatory or autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Nerve conduction studies to determine whether nerves are being compressed or damaged
- Joint fluid analysis to identify infection or crystal-related joint diseases
6. How Is Generalized Musculoskeletal Pain Treated?
To manage and improve generalized musculoskeletal pain, patients may combine home care measures, prescribed medications, and complementary therapies such as acupuncture. Treatment approaches include:
6.1. Home Care to Support Pain Relief
RICE Method: The RICE protocol consists of four key steps:
- Rest: Allow the body adequate time to recover.
- Ice: Apply ice to the painful area for up to 10 minutes at a time to reduce pain and swelling.
- Compression: Use an elastic bandage to wrap the affected area, helping limit swelling.
- Elevation: Elevate the injured body part, especially when swelling is present, to reduce pressure and promote healing.
Dietary Adjustments: Improving daily nutrition not only helps reduce physical stress from work or study but also lowers the risk of musculoskeletal pain caused by nutritional deficiencies. In addition to consuming a balanced diet that includes all major food groups, it is recommended to increase intake of calcium- and vitamin D–rich foods such as fish, eggs, milk, salmon, mushrooms, and yogurt to support bone and joint health.
Gentle Exercise: Once pain begins to subside, gentle exercises and appropriate stretching can be introduced to restore flexibility, support recovery, and prevent joint stiffness or re-injury.
6.2. Medication
Depending on the severity of symptoms, doctors may prescribe medications such as:
- Pain relievers (e.g., Paracetamol, Tramadol)
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as Ibuprofen, Naproxen, or Diclofenac
- Muscle relaxants (e.g., Coltramyl, Mydocalm)
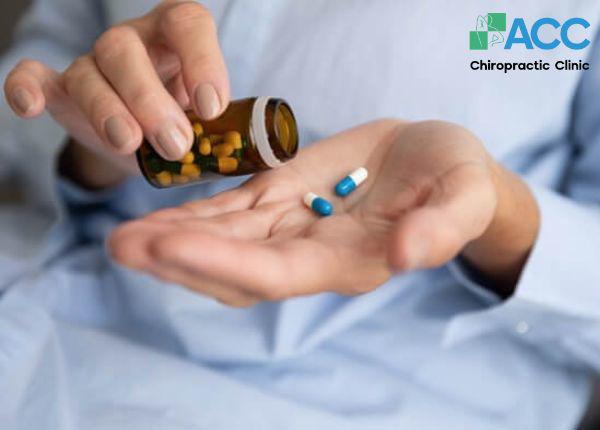

It is important to note that these medications mainly provide temporary symptom relief, and pain may return once the medication effect wears off.
Moreover, improper or prolonged use of medications can cause adverse effects on the digestive system, liver, kidneys, and other organs. Therefore, patients should strictly follow their doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of use.
>> More information: How to treat lower back pain without drug
6.3. Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves the insertion of very thin needles through the skin at specific acupuncture points on the body. The needles may be gently manipulated by hand or stimulated using a mild electrical current. When performed correctly, acupuncture can help improve conditions such as osteoarthritis and nerve-related pain, and may reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines as well as tension headaches.
6.4. Surgery
If generalized Musculoskeletal Pain is a manifestation of a serious musculoskeletal disorder, surgical intervention may be considered. However, due to the potential risks and complications associated with surgery, it is typically recommended only when conservative and non-invasive treatments fail to provide satisfactory results.
6.5. Chiropractic Treatment
Currently, conservative approaches to managing Musculoskeletal Pain are widely adopted in Western countries. Among these, Chiropractic care is highly valued by many healthcare professionals for its safety, effectiveness, and non-invasive nature.
Chiropractic treatment is based on correcting misalignments in the spine and joints, restoring proper joint mobility, and relieving nerve compression-the primary cause of musculoskeletal pain. As a result, Chiropractic care not only alleviates pain effectively but also helps prevent recurrence, without the need for medication or surgery.
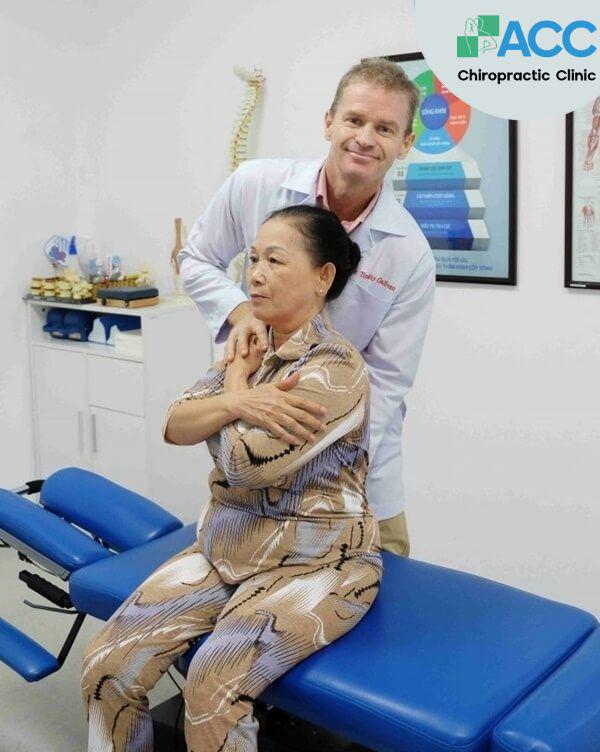
ACC Clinic has been a pioneer in applying Chiropractic care since 2006 and is currently a member of FV Hospital, one of Vietnam’s leading healthcare systems. With a team of 100% international Chiropractors, each with over 20 years of experience in the field, ACC is confident in delivering safe, effective, and personalized treatment solutions for patients of all ages.
In addition, ACC is equipped with modern infrastructure and advanced medical technology, enhancing treatment effectiveness while ensuring a comfortable experience during every session. The combination of international expertise, state-of-the-art equipment, and a professional care environment sets ACC apart as a leading destination for musculoskeletal health in Vietnam.
6.6. Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation
At ACC Clinic, in addition to treating generalized musculoskeletal pain through Chiropractic care, doctors integrate physiotherapy and rehabilitation programs to accelerate the recovery process. Depending on each patient’s specific condition, appropriate therapies are selected to relieve pain, restore mobility, and maintain long-term treatment outcomes.
Treatment is delivered using some of the most advanced medical technologies available in Asia, including DTS spinal decompression systems, ATM2 movement therapy, fourth-generation high-intensity laser therapy, Shockwave therapy, Vertetrac, and Cervico 2000. These non-invasive modalities provide fast, safe, and effective pain relief while avoiding the risks and side effects associated with surgery or long-term medication use.
In addition, patients receive professional guidance on performing therapeutic exercises with correct posture and proper technique. This ensures optimal treatment effectiveness, significant pain reduction, prevention of recurrent injuries, and comprehensive recovery of the musculoskeletal system.
7. How to Prevent Musculoskeletal Pain
To reduce the risk of joint and musculoskeletal pain, it is important to maintain an active lifestyle, follow a balanced diet, and keep a healthy body weight.
- Regular Exercise: Appropriate physical activity helps maintain flexibility in muscles and joints, strengthens supporting muscles, and protects joints from injury.
- Maintain Proper Posture: Correct posture when sitting, standing, lifting, or carrying objects helps reduce stress on joints and prevents injuries caused by poor posture or repetitive movements.
- Balanced Nutrition: A healthy, well-balanced diet provides essential nutrients for bones, muscles, and joints, supports overall health, and reduces the risk of degeneration and musculoskeletal pain.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess body weight places additional stress on joints such as the knees, hips, and spine, increasing the risk of pain and injury.
- Avoid Overuse and Repetitive Strain: Limiting repetitive movements, heavy lifting, or prolonged physical strain helps protect joints, muscles, and soft tissues from injury.
8. Frequently Asked Questions About Generalized Musculoskeletal Pain
Many patients have concerns related to generalized joint and musculoskeletal pain, including:
8.1. Why Is Musculoskeletal Pain Becoming More Common Among Young People?
The increasing prevalence of joint pain in younger individuals is largely related to lifestyle factors such as lack of physical activity, poor posture (slouching, prolonged sitting), and unhealthy dietary habits (frequent consumption of fried foods and sugary beverages).
8.2. How Can Musculoskeletal Pain Be Reduced at Night?
Home-based methods such as alternating hot and cold compresses, along with gentle stretching exercises, may help relieve joint pain at night. If symptoms persist or worsen, patients should consult a doctor and avoid self-medicating without professional guidance.
8.3. Where Should I Go for an Examination If I Have Generalized Muscle Pain?
Patients may consider the ACC clinic system, which has over 20 years of experience in treating musculoskeletal conditions. ACC’s team of experienced doctors provides thorough assessments and tailors treatment plans to achieve effective and long-lasting results.
8.4. Can Generalized Musculoskeletal Pain Resolve on Its Own?
Mild musculoskeletal pain not related to underlying disease may resolve within a few hours or days. However, pain caused by musculoskeletal disorders often persists for weeks, gradually worsens, and may be accompanied by other concerning symptoms. Early medical evaluation is therefore essential.
8.5. What Are the Possible Complications If Musculoskeletal Pain Is Left Untreated?
If left untreated, moderate to severe musculoskeletal conditions can lead to chronic pain, reduced mobility, and long-term functional limitations, significantly affecting quality of life and work capacity.
9. ACC Advice
Do not ignore generalized musculoskeletal pain, as it may be an early warning sign of underlying health conditions. Seeking evaluation from a specialist as soon as symptoms appear allows for timely and effective treatment.
The information above provides a clear understanding of what bone and joint pain is. In summary, generalized bone and joint pain is a common condition, but it can be effectively managed and even prevented through a healthy lifestyle, appropriate exercise, and proper body care. Paying close attention to nutrition, posture, and early warning signs from the body will help protect the musculoskeletal system, reduce the risk of recurrence, and enhance overall quality of life each day.






