Contents
- 1. Common Knee Injuries
- 1.1. Fractures
- 1.2. Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
- 1.3. Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injuries
- 1.4. Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injuries
- 1.5. Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Injuries
- 1.6. Knee Dislocation
- 1.7. Meniscus Tears
- 1.8. Iliotibial Band (ITB) Syndrome
- 1.9. Arthritis
- 1.10. Bursitis
- 1.11. Sprains
- 2. How to Diagnose a Knee Injury
- 3. What are the Effective Methods for Treating Knee Injuries?
- 4. Ways to Prevent Knee Injuries
Knee injuries can manifest in many different forms. Some mild cases can be treated at home. However, the majority of knee injuries require medical intervention to ensure complete healing and to minimize the risk of complications that could affect the joint’s mobility.
1. Common Knee Injuries
1.1. Fractures
The knee joint is composed of three main bones: the femur (thigh bone), the patella (kneecap), and the tibia (shin bone). All three are susceptible to cracking or closed fractures due to falls, motor vehicle accidents, or high-impact collisions.
In practice, doctors report that the incidence of closed fractures in the patella is significantly higher than in the other bone segments. Furthermore, osteoporosis can also be a contributing factor to this type of injury.
1.2. Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is responsible for the flexion and extension movements of the knee joint and prevents the tibia from sliding forward relative to the femur. Injuries to this soft tissue band are categorized into three different grades:
- Grade 1: Ligament sprain due to overstretching.
- Grade 2: Small tears begin to form in the ACL.
- Grade 3: The patient suffers a complete ligament rupture.
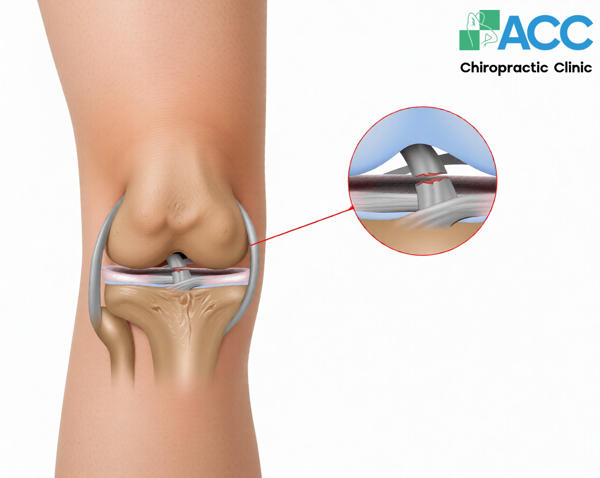
Athletes in high-contact sports such as football and hockey are the most susceptible to ACL injuries. However, sports-related trauma is not the only cause; suddenly changing direction while moving at high speeds can also result in a ligament tear.
1.3. Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injuries
As the name suggests, the Posterior Cruciate Ligament is located at the back of the knee joint. The role of this connective tissue band is also to stabilize the knee structure by preventing the tibia from sliding too far backward.
PCL injuries typically occur due to a heavy impact on the front of the knee or overextension of the knee joint during sports activities or accidents.
>> Reference Information: Is a PCL Rupture Dangerous? Early Warning Signs
1.4. Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injuries
The primary function of the medial collateral ligament is to connect the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone) along the inner aspect of the knee. An MCL injury typically occurs due to a direct impact on the outer side of the knee joint. This force causes the knee to twist or collapse inward, leading to the ligament being overstretched or torn.
1.5. Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Injuries
The lateral collateral ligament serves to stabilize the outer side of the knee. It can be injured when the inner side of the knee sustains a heavy blow, forcing the knee to rotate outward, or due to sudden changes in posture during physical activity. Although LCL injuries occur less frequently compared to other ligament injuries, the severity of the damage can be extremely serious.
1.6. Knee Dislocation
A knee dislocation occurs when the femur (thigh bone) and the tibia (shin bone) slip out of their original positions. The most common causes of this condition are a deformed knee joint structure or trauma resulting from a high-impact collision.
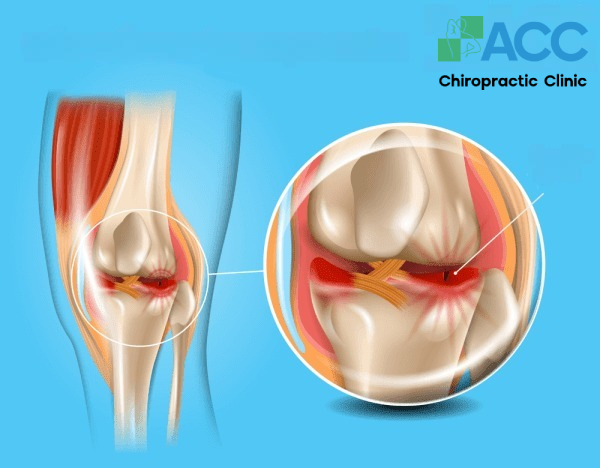
1.7. Meniscus Tears
A meniscus tear is another common type of knee injury. The meniscus is responsible for protecting the ends of the tibia and femur, preventing them from rubbing against each other during movement to avoid bone attrition, which can lead to degeneration.
Heavy pressure is the primary cause of a meniscus tear. This is often related to high-impact activities or improper movement habits, such as frequently standing up too quickly from a deep squatting position.
On the other hand, a torn meniscus can sometimes be a consequence of knee osteoarthritis (joint degeneration).
1.8. Iliotibial Band (ITB) Syndrome
The iliotibial band is a layer of connective tissue that extends from the hip down to the tibia on the outer side of the knee. In the knee area, it plays a crucial role in supporting joint movement.
Repetitive knee flexion and extension over a long period can cause injury to this soft tissue band, leading to Iliotibial Band Syndrome. This condition causes pain on the outer side of the knee joint, which can radiate up to the thigh or buttocks. Track and field athletes, especially long-distance runners, are the most susceptible to this condition.
1.9. Arthritis
Arthritis causes the joint and its surrounding areas to swell, leading to extreme discomfort. In this state, patients not only experience pain but also face joint stiffness, restricted mobility, and occasionally a “grating” or “popping” sensation (crepitus) inside the knee when moving. Besides genetic factors, previous injuries can also contribute to the development of osteoarthritis.
>> Learn more about: What to Eat, Drink, and Avoid to Increase Joint Fluid for Dry Knee Joints?
1.10. Bursitis
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions between bones and soft tissues such as ligaments, tendons, and muscles. The function of the bursa is to facilitate smooth movement and provide nourishment to the joint cartilage. Due to various causes such as excessive pressure or trauma, the bursa can become inflamed, leading to pain or swelling in the joint area.
1.11. Sprains
Everyone is at risk of a knee sprain during sports, manual labor, or falls. The cause is a sudden force that stretches or tears one or more ligaments in the knee, leading to a sprain. The severity of a sprain varies from person to person, ranging from mild and moderate to extremely severe.
2. How to Diagnose a Knee Injury
After sustaining a knee injury, patients should visit the nearest medical facility for an examination. Here, patients will undergo imaging tests to determine the exact location and extent of the damage. Specifically:
2.1. X-ray
An X-ray is a diagnostic imaging method that should be performed immediately after an injury. It helps assess the extent of bone and joint damage quickly and effectively.
2.2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Unlike X-rays, an MRI scan is typically performed 2 to 3 weeks after the injury occurs, once the swelling (edema) has subsided and there is no longer a hematoma (blood collection) within the joint. The test results allow doctors to detect potential damage to the soft tissues surrounding the knee, such as cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and muscles.
3. What are the Effective Methods for Treating Knee Injuries?
3.1. Initial Management (Home Treatment)
If the knee pain resulting from the injury is not too severe, patients can alleviate the pain at home using the following methods:
- Rest: Allow your knee to rest by limiting movement, avoiding strenuous actions in the knee area, or any activities that put pressure on the joint to minimize pain.
- Cold Compress (Icing): Apply a cold compress within the first 24 hours after the injury to reduce swelling and pain. Icing should be done consistently for 2–3 days following the trauma. Note that each session should only last 20–30 minutes, with a 3–4 hour break between sessions.
- Elevation: Place a pillow under your leg while lying down or sitting to reduce pain and swelling.
- Bracing: You should wear a knee brace to stabilize the injured area and prevent further trauma to the knee.
- Medication: Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers may be used. However, to avoid risks such as gastric ulcers or kidney damage, it is best to consult a doctor to prevent potential side effects.

If the knee pain persists for more than a week or becomes more severe, patients should visit the nearest medical facility for a check-up and to receive a proper treatment plan.
3.2. Conservative Treatment
This treatment approach is applied when damage to the ligaments or joint cartilage is not severe enough to require surgery. In these cases, doctors will utilize conservative methods:
- Immobilization: During the first three weeks, the doctor will immobilize the patient’s knee using a brace or a cast.
- Rehabilitation: After three weeks, the doctor will guide the patient through gentle exercises to restore function, regain range of motion (ROM), and strengthen the muscles to prevent muscle atrophy (wasting).
Daily knee pain relief exercises with ACC Clinic:
3.3. Surgery
If, following an injury, the knee ligaments or meniscus are torn and cannot heal on their own, surgery must be performed. Typically, arthroscopic surgery is the procedure of choice, conducted once the swelling has subsided and the joint’s range of motion has been relatively restored. Specifically, cases that are commonly indicated for surgery include:
- Grade 2 and Grade 3 ACL injuries.
- PCL injuries that cause joint instability (loose joints).
- Meniscus tears or articular cartilage fractures that lead to joint locking.
3.4. Rehabilitation Exercises
Exercise is crucial for patients with knee joint injuries, whether they undergo surgery or not. This process strengthens the lower limb muscles and maintains the knee’s range of motion, thereby helping patients return to their normal daily activities sooner.
In cases where the injury is treated surgically, the doctor will design specific rehabilitation exercises to stabilize the joint structure and improve mobility. The intensity of the training will be adjusted depending on the stage of recovery, allowing the patient to regain movement levels nearly identical to those before the injury.
Knee Rehabilitation Exercises
3.5. Drug-Free and Non-Surgical Treatment for Knee Injuries
Because the risks associated with pain medication and surgery can potentially have serious impacts on a patient’s health, people with knee injuries today often seek more effective and safer alternative treatments.
In Vietnam, ACC Clinic is a leading specialist in the field of treating the root causes of musculoskeletal issues, including knee injuries, without the need for drugs or surgery.
For each specific type of knee injury, doctors at ACC Clinic will recommend different treatment approaches, such as:
a. Injuries Related to Misalignments in the Joint Structure
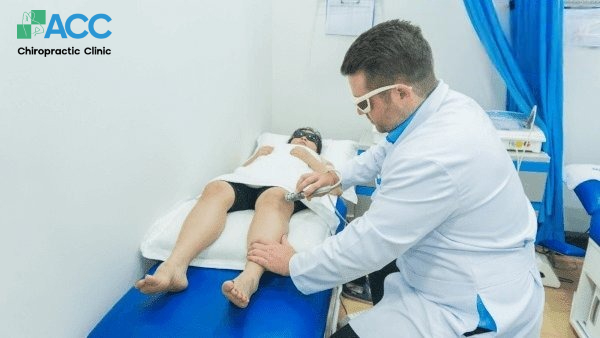
Misalignments in the knee joint structure can result from dislocations or as a consequence of issues such as ligament damage or worn-out cartilage. In these cases, realigning the displaced components of the knee is essential. Chiropractic care is considered a safe and effective solution. In this method, doctors use their hands to apply controlled force to adjust the joint structures back into their correct positions, while simultaneously activating the body’s natural healing ability for the knee joint and surrounding areas. As a result, pain and inflammation are eliminated completely without the need for medication or surgical intervention.
Boasting a team of 100% foreign-trained Chiropractic specialists with many years of experience, ACC is one of the few medical facilities capable of maximizing the effectiveness of this treatment for knee injuries.
b. Injuries Related to Soft Tissue Damage
In cases involving damage to soft tissues such as ligaments or the iliotibial band, ACC doctors will develop a comprehensive treatment plan. This approach combines Chiropractic care with Shockwave Therapy and Class IV High-Intensity Laser Therapy. These advanced technologies stimulate the cell regeneration process, thereby accelerating the recovery of the injured tissues.
4. Ways to Prevent Knee Injuries
Since injuries are unexpected events, they can be difficult to prevent entirely. However, you can still build healthy habits to minimize the risk of knee damage, such as:
- Stay vigilant: Observe your surroundings carefully while moving.
- Warm up thoroughly: Always perform a proper warm-up before engaging in sports.
- Use protective gear: Wear appropriate protective equipment as required for your sport.
- Adjust training intensity: Carefully consider and balance the intensity of your workouts.
- Maintain a scientific diet: Ensure a nutrition-rich diet to support and maintain musculoskeletal health.
- Apply RockTape: Use RockTape (kinesiology tape) to prevent injuries and aid in recovery for athletes and sports enthusiasts.

Each type of knee injury can be effectively treated with one or more different methods. The earlier the treatment begins, the higher the effectiveness. Therefore, if you suspect your knee joint is injured, seek out a reputable specialist for a timely, effective, and safe examination and treatment.
>> See more related articles: Long-term relief of knee pain due to osteoarthritis! The ACC approach!





