Contents
The International Federation of Orthopedic Manipulative Physical Therapists (IFOMPT) defines manual therapy techniques as: Skilled hand movements intended to produce any or all of the following effects:
- Improve tissue extensibility.
- Increase range of motion of the joint complex.
- Mobilize or manipulate soft tissues and joints.
- Induce relaxation.
- Change muscle function.
- Modulate pain.
- Reduce soft tissue swelling, inflammation, or movement restriction.
1. Manual Therapy VS. Massage, What’s The Difference?
At first glance it is easy to mistake manual therapy for a massage. However, there are significant differences between these two methods. It is important for you to be able to understand these differences, in order to pick the appropriate treatment method.
1.1. Massage
A massage is the use of rhythmically applied pressure to the skin and soft tissues of the body. The goals of this method are increase circulation and promote tissue relaxation in the muscles.
1.2. Manual Therapy
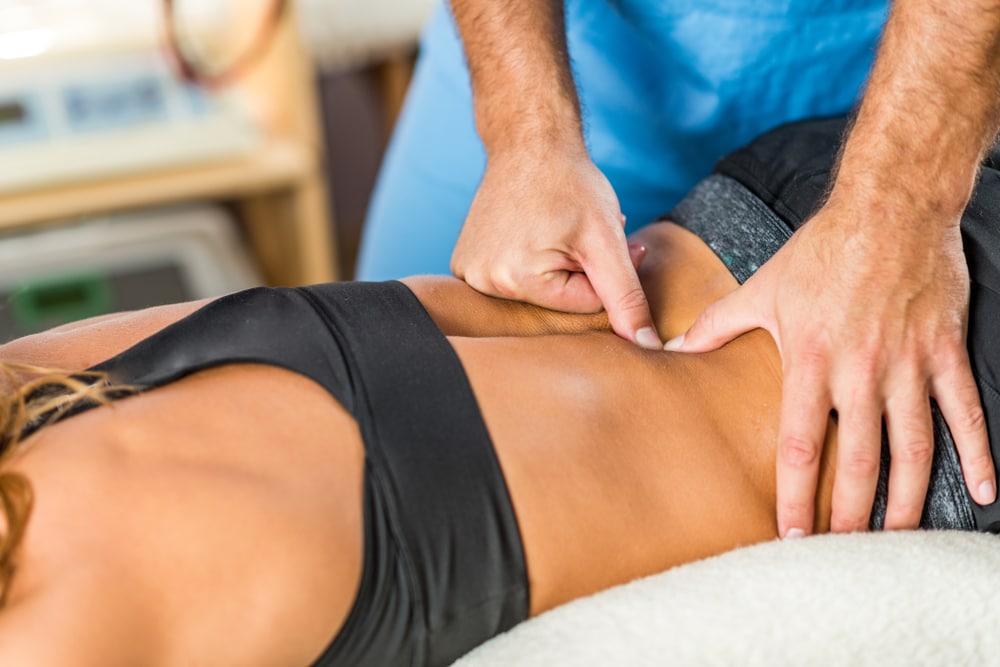
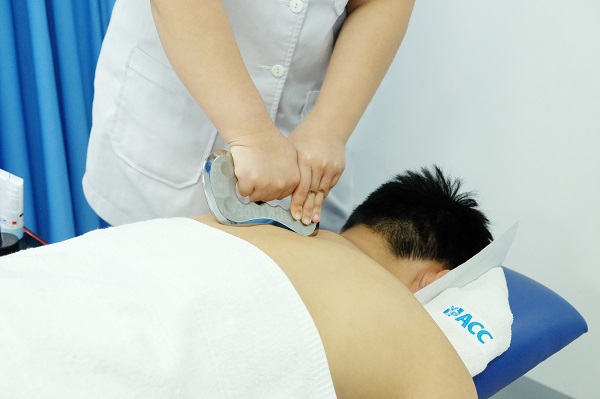
Manual therapy is the application of hands-on techniques to body tissues with the intent to therapeutically assess and treat. Some manual therapy techniques utilized by physical therapists include soft tissue mobilization, myofascial release, stretches, instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization.
Both massage and manual therapy can be utilized as a part of a plan to promote an individual’s overall health and wellness. However, the education and skill level needed to practice manual therapy is much more comprehensive.
2. What Type of Injuries or Problems Is Manual Therapy Helpful?
Manual therapy is important in physical therapy treatment. Your doctor can recommend manual therapy if you suffer from one or many of the following conditions:
- Neck pain
- Low back pain
- Headaches
- TMJ dysfunction
- Hip pain
- Knee pain
- Ankle pain
- Shoulder pain
At ACC, our doctors and physical therapists are highly educated healthcare providers. We have provided our services and given new hope to thousands of patients suffering from debilitating pain and chronic spinal problems.
Read more: